Like the physical robots that have been replacing industrial jobs, virtual robots will eventually replace a large number of business jobs.
We refer to this substitution as RPA (Robotic Process Automation). With the use of specific tools, companies can achieve incredible results with this type of technology. Yes, it is true that there are other forms of automation, but these require the monitoring of employees.
There are some RPA tools on the market that can be used even by “non-programmers” (that is, people who have no programming background), giving them the possibility to also develop robots capable of automating any repetitive virtual process.
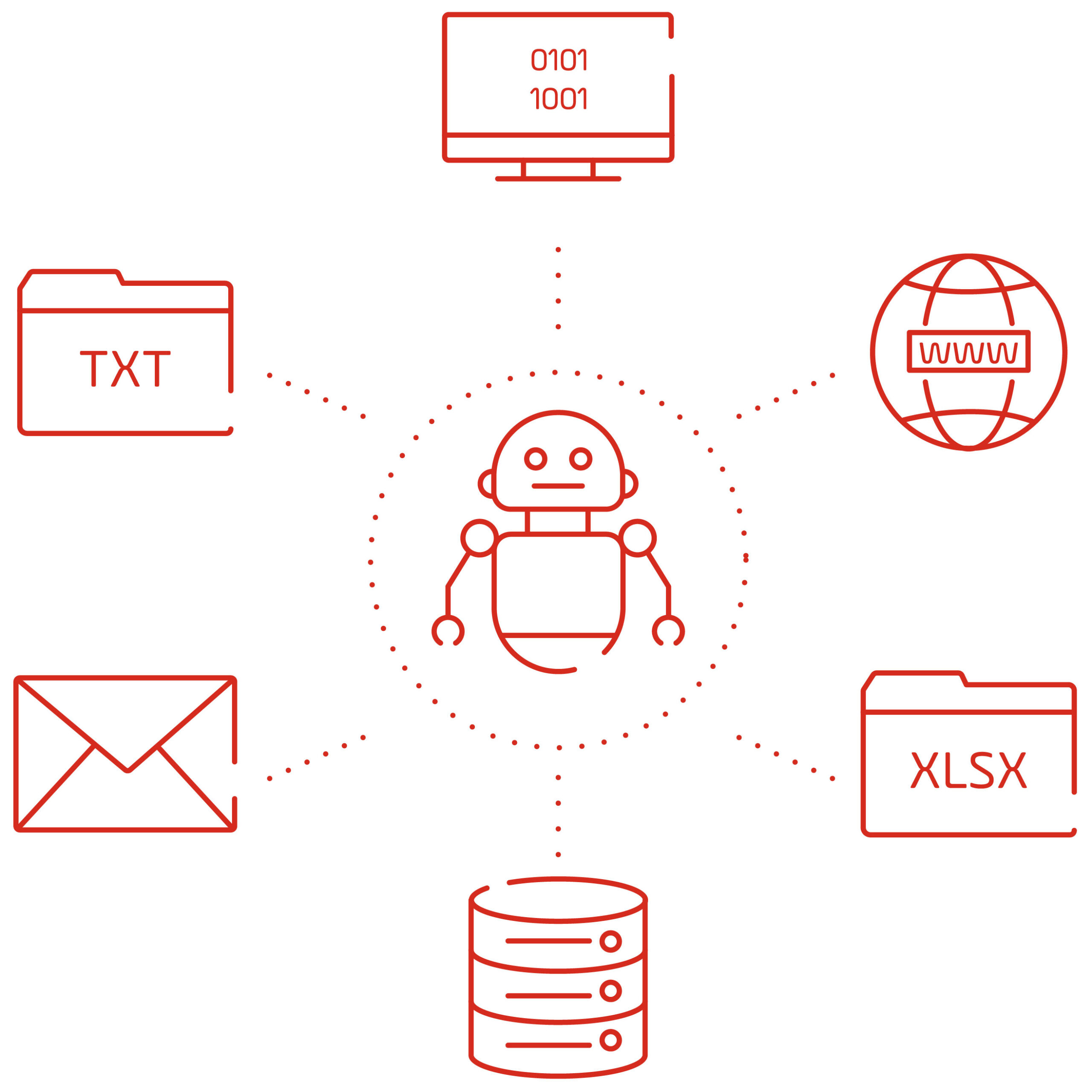
These processes are usually performed by a human being, even if they require the interaction of various systems or technologies such as desktop applications, websites, excel files, emails, and databases.
They help us perform certain tasks in a cheaper, faster, and more consistent way for a longer period of time, making us more efficient and effective.
It has been proven by several business leaders around the world that there are many advantages to surrendering and adhering to this technology, such as efficiency, quality, error reduction, and cost reduction.
We are, therefore, facing a technology that was born in the new era, whose main objective is to imitate what humans do, using our systems and interfaces.

RPA is the use of what we call software robots with AI and machine learning capabilities, which allow us to emulate and integrate actions typically performed by humans. These actions consist mainly of repetitive and high-volume business tasks, based on clear and well-standardized rules established by the previously defined processes.
Robot programmers use various RPA tools to create robots capable of capturing, interpreting, and performing routine tasks performed by humans, and which interact with the various existing systems such as desktop applications, websites, excel files, text files, XML documents or JSON, email, and databases, among others.
Although RPA is associated with robots, in the sense that it performs tasks automatically, we cannot say that they are physical machines getting the job done. It is common to use the term “robots” to describe the automation of virtual processes, and despite it being a bit of a misnomer, it’s used to provide a clearer vision of what this technology really consists of.
Robots can be classified as unattended or autonomous and attended or assistive. The first is an autonomous robot, which is programmed to perform a task without requiring any human intervention.
The attended or assistive robot, as the name implies, requires human assistance at one or more points in the process. This usually involves a decision that requires logical reasoning, that forces the automation to stop at that moment.
In general, there is no restriction where RPA can be applied. It can be used in any business sector or task. Of course, there are also situations where other solutions should be invested in, according to the company’s needs, in order to generate the best return on investment (ROI).
With the advantage of being able to interact with other software and files through the same interface used by a human user, RPA stands out for its versatility compared to other types of automation. These require more effort and expertise, not to mention system integration through APIs, which are not always available.
Other types of automation often require a programming background, and even in that RPA stands out, as there are solutions in this technology that require neither programming experience nor knowledge.
Sectors such as banking, finance, insurance, and BPO are best suited with an RPA model. This is because they are sectors with repetitive processes that involve a high volume of data, and time consumption.
In the case of the financial and banking sectors, they are highly regulated industries, which require security and precision. It is, for example, in these types of tasks that robots stand out more than humans.
Of course, there are other industrial sectors where we can also apply RPA models, such as telecommunications, retail, manufacturing, health, etc. Compared to the sectors that most often seek RPA as a solution, they cannot be said to have other advantages, as they are pretty much the same efficiency and effectiveness.
Due to its versatility, as long as the process involves the operation of software, it is possible to use RPA. In other words, RPA can be implemented in different departments and areas throughout a company as long as it is possible to develop automation based on actions and rules that are normally performed by company employees. Some of these tasks can be, for example:
- Copy/paste data
- Filling out forms
- Application logins
- Web data extraction
- Interaction with multiple systems
- Reading and writing in the database
- Performing calculations
There are many other actions that we can automate with RPA. However, the main objective of this technology is not to replace multiple systems, but to try to improve them.
For a company to survive it must be in constant growth. By implementing an RPA system, companies significantly reduce costs and increase revenues, earning a higher profit margin.
When making this replacement, companies not only have advantages in terms of effectiveness and efficiency but also manage to provide their employees with a better work environment. Here’s how.
The main advantages of implementing an RPA model are:
- Reduction of operating costs
- Scalability
- Reduction of time lost in repetitive tasks
- Focus on tasks that require more thinking and that add more value to the company
- Professional motivation
- Service quality assurance
- Error reduction
- Increased results
- Increased working hours (24h / 24h)
By replacing labor with virtual robots, companies greatly reduce operating costs. In addition, automation can also significantly reduce the time spent on repetitive tasks.
Thus, utilizing robots saves employees time for tasks that require more logical reasoning. This means that, in a certain way, it motivates employees to have a less monotonous and more productive work model, with more time to stimulate their creativity.
Employees gain more autonomy to perform important and strategic functions for the growth of their business (core business), without harming the quality of the services it provides or the product it develops.
Using RPA also allows you, depending on the performance of the robots, to reduce the likelihood of errors and increase the return on investment.
There is also the advantage of a robot’s working time compared to a human. Robots can work 24 hours straight without vacations or breaks. Human beings, on the other hand, due to physical and mental fatigue, should normally limit themselves to 8 hours of work daily, alternating with moments of rest.
In addition to all these advantages, there is another one that, for a software developer and someone curious about business operations, I consider equally important.
When implemented in any sector of a company, RPA has an impact on streamlining the relationship between employees in the various departments of the company, creating an environment open to dialogue.
As with almost everything in life, there are advantages and disadvantages, and RPA also has its less beneficial side. It is estimated that, according to the study ‘The future of Workplaces’ by the WEF (World Economic Forum), there will be a significant increase in jobs around the world that will be replaced by automation by 2025.
This study was carried out before the pandemic, which probably accelerated this process and anticipated its results.
Often there are those who confuse automation testing with process automation. Very briefly, I will explain what each one consists of.
Automation tests consist of repeating the same tests several times on different types of operating systems, mobile apps, or different browsers. These tests allow us to assess whether the product is ready to be placed in a production environment or not.
Automation in RPA consists of the development of robots capable of performing real tasks that were previously performed by employees, with the advantage of working in any department of the company.
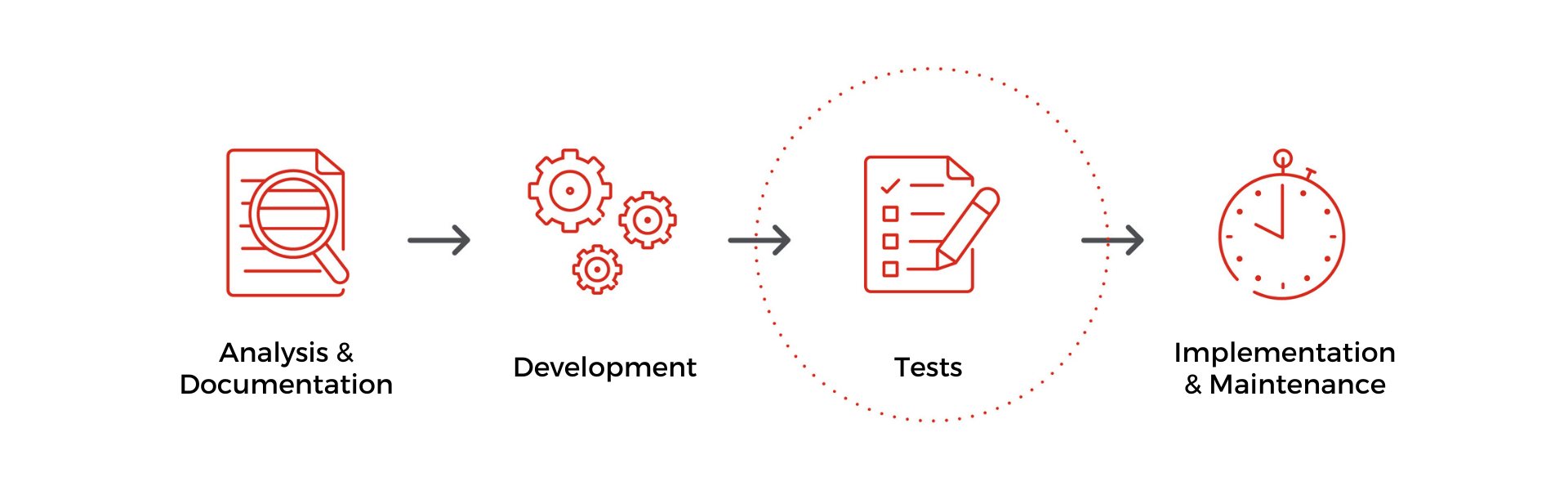 The main steps are:
The main steps are:
Analysis and documentation—First, we create the requirements survey. We analyze the processes, define them and assess to see if they have the potential to be automated. Each process that has the potential to be automated is documented. The architecture is created and the environment is prepared according to each process. Finally, the entire workflow is designed.
Development—The process is developed according to specific rules, taking into account restrictions, until it is completely automated.
Tests—The automation is extensively tested and prepared until it is ready to be placed in a production environment.
Implementation and Maintenance—The automation of the process is implemented in the production environment, made official and monitored, and everything important is documented. The performance of the process automation is evaluated, and if necessary, changes are made to the automation in order to correct or improve it.
There are numerous tools in the RPA world, but what follows are some that present bigger and better solutions, each in their own way. Some of these names are UiPath, Automation Anywhere, Blue Prism, Pegasystems, Workfusion, Another Monday, and Kryone, among many others.
I highlight the first three because they are currently the most prominent in the market and are considered the best solutions for automating processes in the main business sectors worldwide.
UiPath—It is currently the most widely used tool on the market worldwide, mainly used in the finance, insurance, health, telecommunications, manufacturing, public sector, and BPO sectors. They provide us with products such as Platform, Studio, StudioX, Robot, and Orchestrator.
It presents us with a set of automation solutions such as Desktop, Web, GUI, Citrix, Excel, Email, and SAP, among many others. In addition to being attractive and very intuitive, it has a flexible interface.
Automation Anywhere—It operates mainly in the BPO, financial services, health, manufacturing, public services sectors. Like UiPath, it also uses technology capable of developing assisted and unattended automation.
Automation Anywhere introduces us to products like AA Enterprise, IQ Bot, BotFarm, Bot Insight, and the Bot Store. With a list-like interface, this is one of the three popular tools that most resembles web development software.
Blue Prism—A pioneer in the development of process automation software, this tool is used mainly in the banking, e-commerce, and investments sectors. It supports platforms such as JAVA, Windows, and Mainframe. It presents a flowchart interface with drag and drop functionality, and uses the C # programming language as a base.
UiPath and Automation Anywhere are both American software development companies, while Blue Prism is based out of England. The RPA tools, like all technology, are constantly evolving and are increasingly part of the day-to-day management assistance, and consequently, the success of large national and international companies.
Working for almost a year with UiPath, I believe that this is the tool on the market that not only presents the best solutions but also provides flexibility in the various stages of the RPA process, taking into account the wide range of products it offers (some of which are free, such as Community Edition).
To design, develop, and monitor projects, UiPath offers us three main components: UiPath Studio, UiPath Robot, and UiPath Orchestrator.
UiPath Studio has great tools for the development of automation and contains several activities that help in the development of projects.
In addition, we can program numerous tasks that a human being would normally do, such as entering websites with dynamic pages through the web Record or UiExplorer functionality or entering desktop applications that are not normally detectable that are accessible with UiPath.
We also have a powerful robot management and control system, called the UiPath Orchestrator. We can use it as a mobile app to run, schedule, and cancel our robots wherever and whenever we want.
There would certainly be much more to talk about UiPath as a whole, but I leave that for a future article.
RPA is ultimately about technology that portrays the future. Little by little, the human being is being replaced by machines, and due to the accelerated development of technology, this substitution is also accelerating.
That said, it is certain that RPA will have advantages and disadvantages. The question is: will we have more advantages than disadvantages?
Many say that robots came to improve our quality of life, but many also fear that this improvement could also have consequences. Is it the right exchange in the business world? I believe that what we can do for now is to wait and see.
Until then, if you have more questions about what value RPA can add to a company, feel free to comment on this article or to contact us directly.